
Mnova MS: For processing and analysis of LC/MS and GC/MS data from most vendor formats. Second-order spectra Hoye's method what are typical couplings problem solving 1.Mnova NMRPredict Desktop: For prediction of H-1, C-13, N-15, O-17, F-19, Si-29, P-31 chemical shift and H-1 coupling constants. Magnetic equivalence the Fermi contact model first- vs. Kwan energy diagrams for J coupling the chemical shift Helpful References chemical vs. Coupling Constants Scope of Lecture Eugene E. Kwan Lecture 3: Coupling Constants Chem 117 January 31, 2012.
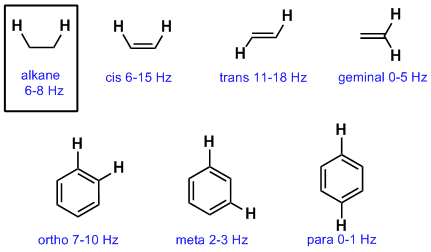
Why does a peak for a particular set of protons split into a multiplet? How many different kinds of 13c peaks will be seen? The J(NH-H) coupling constants were obtained from 1D spectra recorded. How do you identify splitting patterns?processed using MestReNova (Mestrelab) on a Mackintosh G5 desktop computer. A coupling constant that is ranging between 1-3Hz indicates that the arrangement of protons are in the meta position. The stereospecific evidence lies in the coupling constants of the hydrogens in the aromatic ring, which are between 1-3 Hz.
What does a doublet of doublets look like?The number of peaks tells you the number of different environments the hydrogen atoms are in. How do you calculate the doublet coupling constant? How do you find the J value in MestreNova?

Both of these would produce four peaks. In A and B, there are four totally different environments. … How many different kinds of 13c peaks will be seen?In the spectrum there are a total of three peaks – that means that there are only three different environments for the carbons, despite there being four carbon atoms.

What do J values tell you?The coupling constant J is pretty much the peak-to-peak distance, usually reported in Hz. It is an indirect interaction between two nuclear spins that arises from hyperfine interactions between the nuclei and local electrons. What causes j coupling?In nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, J-couplings (also called spin-spin coupling or indirect dipole–dipole coupling) are mediated through chemical bonds connecting two spins. The peaks within a triplet or quadruplet all have the same spacing, so you’ll only need to calculate this value once. If the second peak results in a value of 502.68, for example, the value for J would be 2.02 Hz.
The first thing to do is convert the peaks from ppm into hertz. The trick is that J is measured in Hz, not ppm. How do you find the J value for a doublet?Calculation of Coupling constant: For the simple case of a doublet, the coupling constant is the difference between two peaks. The implications are that the spacing between the lines in the coupling patterns are the same as can be seen in the coupling patterns from the H-NMR spectra of 1,1-dichloroethane (see left). What do J values tell you in NMR?The coupling constant, J (usually in frequency units, Hz) is a measure of the interaction between a pair of protons.
An example is the NMR spectrum of methyl acrylate. What causes a doublet of doublets?A doublet of doublets (dd) occurs when a hydrogen atom is coupled to two non-equivalent hydrogens. Drag a box around each group of equivalent protons. To do this, go to Analysis → Multiplet Analysis → Manual (or just hit the “J” key). The easiest one is to use the Multiplet Analysis tool. How do you find the J value in MestreNova?To calculate coupling constants in MestreNova, there are several options.
Also the dmso which have more exchanged proton like d4 or others can be shown but it is out of normal range. So the peak at 2.5 ppm indicates dmso-d5 not d6. Why does DMSO give Quintet?I learned that dmso peak in 1H NMR caused by proton exchange. If both of the coupling constants are the same, a triplet (t) occurs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
